Where can champagne be made?
Dear champagne lovers,
While champagne wine is known throughout the world, the terroir from which it is made is much less well known. And as you may know, champagne wine is recognized as A.O.C.
The appellation d’origine contrôlée (AOC) allows to link a product to a geographical area and subjects it to rules of production and elaboration. A product recognized as AOC is therefore the expression of a link between a production and a land, all implemented and perpetuated by the know-how of men.
You are wondering what are the rules to respect to obtain an AOC? where is the champagne made? And what equipment is necessary for the elaboration and bottling of champagne? Don’t look any further, you’ve come to the right place!
As a native of the Champagne region, I’m going to tell you everything I know. And if you are not yet informed about the process of making a champagne wine, I invite you to read my article: the secrets of champagne making.
What are the rules for champagne to obtain an AOC?
The rules of an AOC are not only limited to a geographical area, but they concern each step of the production. It is the terroir in the broadest sense that is taken into account, by integrating several components: technical, geographical, human, climatic … What are the rules for champagne wine?
A strictly delimited geographical area:
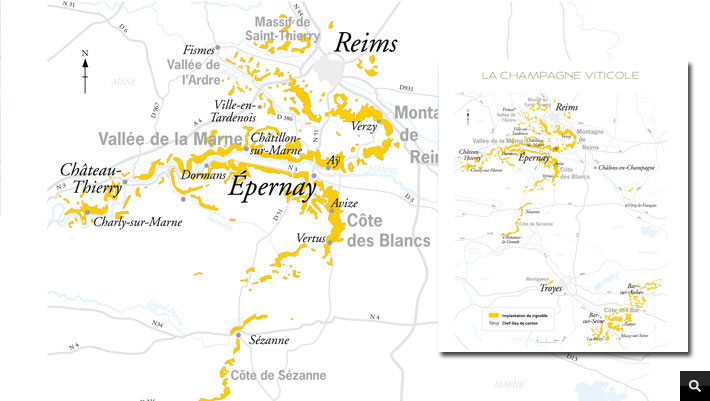
The Champagne terroir is located mainly in the Grand-East region and extends over 5 departments: the Marne, representing alone 66% of the vineyard, the Aube, which represents 23% and the Aisne, 10%. The Haute-Marne and the Seine-et-Marne together represent only 1% of the Champagne vineyard.
A defined terroir:
The grapes must come from vines that are located in a very precise terroir validated by the Champagne Committee. To obtain the Champagne appellation, they must only be harvested in one of the four main regions: the Côte des Blancs, the Montagne de Reims, the Vallée de la Marne and the Côte des Bar.
Authorized grape varieties:
The main grape varieties harvested are pinot noir, pinot meunier and chardonnay. However, these are not the only authorized grape varieties, there is also arbane, petit meslier, pinot blanc and pinot gris, but they represent only 0.3% of the vineyard.
Pruning of Champagne vines:
As with the major regions, there are 4 types of authorized Champagne pruning: Chablis, Cordon, Guyot and Vallée de la Marne. The latter is only valid for pinot meunier.
Techniques:
They are numerous and are governed by the Champagne Committee, I will quote some of them: limitation of the density of plantations to 8,000 vines / hectare, pruning system including precise gestures regulated since 1938, yield at pressing of 160 kilos for 102 liters, second fermentation in bottles and maturation on lees for 15 months minimum for non-vintage, 3 years for vintage… You will have understood, is not champagne who wants!
What is the necessary equipment to make champagne?
How to transform the grapes into champagne wine ?
After the harvest, it is the pressing. The grapes will be crushed in a press to be transformed into must. Then, the must is collected to be stored in a large tank for several months. A liqueur de tirage, composed of wine, sugar and yeast, is added to make the wine effervescent. This is when the wine becomes champagne. This process is called prise de mousse.
How to bottle a production ?
To bottle champagne, you must first fill the bottles and then close them. Each step requires equipment, I’ll walk you through them.
The filling :
In order to perform this step, you have to make sure that the bottles are perfectly clean. Then, each bottle will be filled with the help of a filler, automatic or manual, which will pour the champagne wine. The bottle will be placed at an angle to let the champagne flow down the wall. The flow of the filler should not be too fast, as this could alter the taste and a space should be left to be able to close the bottle with the cork.
The corking :
Once the bottle is filled, it will have to be closed with a cork. Besides, did you know that this cork was born with the champagne? Its role is very important, because it allows to preserve the quality of the wine.
To proceed to the corking, a corking machine will be used. It will allow to close perfectly the bottles: before the installation, the cork is a cylinder; after the installation, under a strong pressure, it changes shape to adhere to the neck and take its shape.
Now that the cork is installed, it is necessary to protect the bottles from air and possible parasites. For this, a cap will be fixed over the cork, using a capper.
The corked bottles will rest upright for a few hours before being installed in a horizontal position and will also be labeled. If you don’t know what are the mandatory and optional mentions on a champagne label, I invite you to discover them here. The bottles will then rest in the cellar, at least 15 months for a brut champagne and 36 months for a vintage champagne.
You know now what are the conditions to respect to make champagne, you know the names of the regions of the champagne vineyard and its place of production. You liked this article and you want to learn more? Check out my other articles on how to preserve champagne, where to buy bottles, what to eat with champagne and is champagne good for your health?




